PyQt
The pyqt
package provides various modules for convenient working with PyQt based graphical user
interface (GUI)
applications. The contents of this subpackage is shown in the following:
import doocspie
help(doocspie.pyqt)
Help on package doocspie.pyqt in doocspie:
NAME
doocspie.pyqt - Modules for convenient working with PyQt based GUI applications.
PACKAGE CONTENTS
concurrency
e_log_printer (package)
messages
FILE
/home/cbehrens/Home/Repositories/gitlab/doocspie/doocspie/pyqt/__init__.py
The concurrency module consists of a PyQt Timer class for
repetitive executions of functions. A fully-fledged
e-log printer that can simply be integrated in any PyQt application is provided by the
ELogPrinter
class, and the
messages
module aggregates commonly used PyQt message dialogs.
Concurrency
A simple and convenient way to repeatedly carry out a function in a GUI can be
realized with the Timer class of the
concurrency module, and its entire documentation
is presented here:
help(doocspie.pyqt.concurrency)
Help on module doocspie.pyqt.concurrency in doocspie.pyqt:
NAME
doocspie.pyqt.concurrency - Module with concurrency support for convenient working with PyQt GUI applications.
DESCRIPTION
This module provides the concurrency support for convenient working with PyQt GUI applications.
CLASSES
builtins.object
Timer
class Timer(builtins.object)
| Timer(function)
|
| Timer class for higher level concurrency support for PyQt.
|
| This class provides the higher level concurrency support for Timers in PyQt.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, function)
| Constructor of the timer class.
|
| This constructor initializes the instance with the function to repeatedly carry out.
|
| Args:
| function (function): The function to repeatedly carry out.
|
| is_active(self)
| Return the timer's activity state.
|
| Returns:
| bool: The state of the timer's activity.
|
| start(self)
| Start the timer with its associated function.
|
| Returns:
| None
|
| stop(self)
| Stop the timer with its associated function.
|
| Returns:
| None
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
FILE
/home/cbehrens/Home/Repositories/gitlab/doocspie/doocspie/pyqt/concurrency.py
The following section introduces the Timer class by means of a fully self-contained code
example.
Timer
The Timer class provides three methods, and their
instances are commonly used in PyQt based GUI application for
repetitive executions of functions. In the following, a fully self-contained GUI
example is presented, which makes use
of the Timer
class and utilizes all of its three methods:
import sys
import time
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout,
QWidget)
from doocspie.pyqt import Timer
class Tool(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self._seconds = 0
self._seconds_label = QLabel("Seconds: " + str(self._seconds))
self._start_button = QPushButton("Start")
self._stop_button = QPushButton("Stop")
self._timer = Timer(self._clock) # repeatedly carry out the 'self._clock' method
self._now = time.time()
self._set_layout()
self._create_connections()
def _set_layout(self):
self._main_layout = QVBoxLayout()
main_widget = QWidget()
main_widget.setLayout(self._main_layout)
self.setCentralWidget(main_widget)
self._main_layout.addWidget(self._seconds_label)
self._main_layout.addWidget(self._start_button)
self._main_layout.addWidget(self._stop_button)
def _create_connections(self):
self._start_button.clicked.connect(self._start)
self._stop_button.clicked.connect(self._stop)
def _clock(self): # repeatedly carried out by the 'doocspie.pyqt.Timer' instance
if time.time() - self._now >= 1:
self._now = time.time()
self._seconds += 1
self._seconds_label.setText("Seconds: " + str(self._seconds))
def _start(self):
if not self._timer.is_active(): # start the Timer if not active yet
self._timer.start()
def _stop(self):
if self._timer.is_active(): # stop the Timer if active yet
self._timer.stop()
def show_window(self):
self.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
application = QApplication([])
tool = Tool()
tool.show_window()
sys.exit(application.exec())
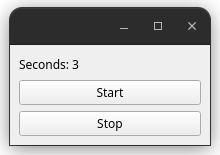
The actual GUI application shown above from the previous code example allows to
start and stop a counter that increments
every second. If desired, a screenshot of such a GUI app can conveniently be
printed into any of DOOCS’ e-logs by
utilizing an instance of the ELogPrinter class.
ELogPrinter
The ELogPrinter class offers a simple method for
conveniently providing a comprehensive GUI dialog for printing to
DOOCS’ e-logs, and its documentation is presented here:
help(doocspie.pyqt.e_log_printer.ELogPrinter)
Help on class ELogPrinter in module doocspie.pyqt.e_log_printer.e_log_printer:
class ELogPrinter(builtins.object)
| ELogPrinter(application_ui, printers, print_exceptions=True)
|
| E-log printer class for providing e-log print dialogs.
|
| This class offers the methods for providing dialogs for printing to e-logs.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, application_ui, printers, print_exceptions=True)
| Constructor of the e-log printer class.
|
| This constructor initializes the instance with the application's ui, the printer (e-log) to print to and the
| optional 'print_exceptions' state.
|
| Args:
| application_ui (subclass of QMainWindow): The application's PyQt ui.
| printers (dict): The e-logs (key) and printers (value).
| print_exceptions (bool, optional): The optional state for handling exceptions with a print dialog.
|
| show_dialog(self)
| Showing a PyQt print dialog of the particular application for printing to a particular e-log.
|
| Returns:
| None
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
The following minimal viable GUI code example demonstrates how to instantiate an
ELogPrinter and showing its dialog.
Such an instance can be integrated in any PyQt based GUI application.
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from doocspie.pyqt import ELogPrinter
class AppUi(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self._application_name = "The App"
self._version = "0.23.42"
@property
def application_name(self):
return self._application_name
@property
def version(self):
return self._version
if __name__ == "__main__":
application = QApplication([])
e_log_printer = ELogPrinter(AppUi(), printers={"FLASH": "ttflog"})
e_log_printer.show_dialog()
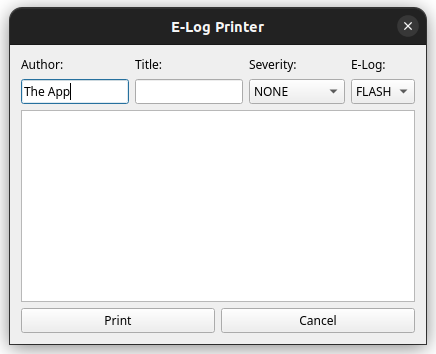
The actual e-log printer dialog shown above from the previous minimal viable code example allows to print a screenshot of the underlying GUI application. The typical DOOCS e-log fields (e.g. author, title, etc.) can be entered into the GUI dialog before actually printing it in the selected e-log.
Messages
Every once in a while, the user of GUI applications must be informed of exceptional
situations, e.g. errors or warnings,
and message dialogs come handy for this kind user interaction. The messages module provides various PyQt message
dialogs and its documentation is presented here:
help(doocspie.pyqt.messages)
Help on module doocspie.pyqt.messages in doocspie.pyqt:
NAME
doocspie.pyqt.messages - Module with message dialogs for convenient working with PyQt GUI applications.
DESCRIPTION
This module provides the message dialogs for convenient working with PyQt GUI applications.
FUNCTIONS
show_about(application_ui, application_name, application_version)
Showing a PyQt about dialog of a given application with its name and version.
Args:
application_ui (subclass of QMainWindow): The application's PyQt ui.
application_name (str): The application's name.
application_version (str): The application's version number.
Returns:
None
show_error(message)
Showing a PyQt error dialog with a given message.
Args:
message (str): The message to show in the PyQt error dialog.
Returns:
None
show_warning(message)
Showing a PyQt warning dialog with a given message.
Args:
message (str): The message to show in the PyQt warning dialog.
Returns:
None
FILE
/home/cbehrens/Home/Repositories/gitlab/doocspie/doocspie/pyqt/messages.py
The following subsection introduces the different PyQt message dialogs of the messages
module.
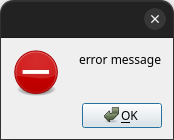
show_error
Error messages can be presented interactively to the user by means of the show_error function, and a minimal viable
GUI code snippet is given in the following:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication
from doocspie.pyqt import show_error
if __name__ == "__main__":
application = QApplication([])
show_error("error message")
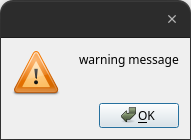
show_warning
Similar to the errors messages above, warning messages can be presented to the
user by utilizing the show_warning
function, and a minimal viable GUI code snippet is shown in the following:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication
from doocspie.pyqt import show_warning
if __name__ == "__main__":
application = QApplication([])
show_warning("warning message")
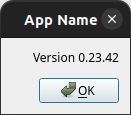
show_about
Typical about dialogs of GUI applications can be opened via the show_about function. The following code example
demonstrates how to incorporate an about dialog into a GUI application:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
from doocspie.pyqt import show_about
class AppUi(QMainWindow):
APPLICATION_NAME = ""
VERSION = ""
if __name__ == "__main__":
application = QApplication([])
show_about(AppUi(), "App Name", "0.23.42")